Muslims perform five prayers a day. Each prayer is given a certain
prescribed time during which it must be performed. This document briefly
describes these times, and explains how they can be calculated
mathematically.
To determine the exact time period for each prayer (and also for fasting), we need to determine nine points of time per a day. These times are defined in the following table:
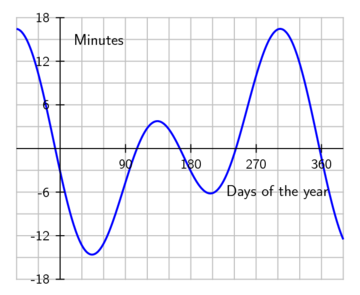
The equation of time is the difference between time as read from a sundial and a clock. It results from an apparent irregular movement of the Sun caused by a combination of the obliquity of the Earth's rotation axis and the eccentricity of its orbit. The sundial can be ahead (fast) by as much as 16 min 33 s (around November 3) or fall behind by as much as 14 min 6 s (around February 12), as shown in the following graph:
To determine the exact time period for each prayer (and also for fasting), we need to determine nine points of time per a day. These times are defined in the following table:
| Time | Definition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Imsak | The time to stop eating Sahur (for fasting), slightly before Fajr. | ||
| Fajr | When the sky begins to lighten (dawn). | ||
| Sunrise | The time at which the first part of the Sun appears above the horizon. | ||
| Dhuhr | When the Sun begins to decline after reaching its highest point in the sky. | ||
| Asr | The time when the length of any object's shadow reaches a factor (usually 1 or 2) of the length of the object itself plus the length of that object's shadow at noon. | ||
| Sunset | The time at which the Sun disappears below the horizon. | ||
| Maghrib | Soon after sunset. | ||
| Isha | The time at which darkness falls and there is no scattered light in the sky. | ||
| Midnight | The mean time from sunset to sunrise (or from Maghrib to Fajr, in some schools of thought). |
Astronomical Measures
There are two astronomical measures that are essential for computing prayer times. These two measures are the equation of time and the declination of the Sun.The equation of time is the difference between time as read from a sundial and a clock. It results from an apparent irregular movement of the Sun caused by a combination of the obliquity of the Earth's rotation axis and the eccentricity of its orbit. The sundial can be ahead (fast) by as much as 16 min 33 s (around November 3) or fall behind by as much as 14 min 6 s (around February 12), as shown in the following graph:
The Equation of Time (Ref)
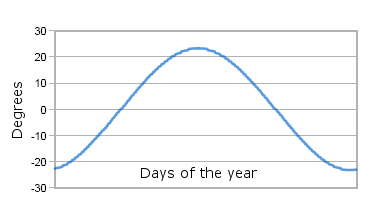
The declination of the Sun is the angle between the rays of the sun
and the plane of the earth equator. The declination of the Sun changes
continuously throughout the year. This is a consequence of the Earth's
tilt, i.e. the difference in its rotational and revolutionary axes.
The Declination of Sun
The above two astronomical measures can be obtained accurately from
The Star Almanac, or can be calculated approximately. The following
algorithm from U.S. Naval Observatory computes the Sun's angular coordinates to an accuracy of about 1 arcminute within two centuries of 2000.

0 comments:
Post a Comment